Internal links play a pivotal role in shaping the structure of a website, influencing user experience, and impacting search engine optimization (SEO). But what are internal links?
Internal links are hyperlinks that connect one page of a website to another page within the same website.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the world of internal links, exploring their definition, benefits, best practices, and their impact on SEO.
What Are Internal Links?
Internal links are hyperlinks that connect one page to another within the same domain.
Unlike external links, which point to pages on different websites, internal links facilitate navigation within a website.
These links are embedded within the content or navigation menus, allowing users to move seamlessly from one page to another.
Benefits of Internal Links
Do internal links help SEO? Here are some benefits of internal links.
Enhanced Navigation
Internal links contribute significantly to user experience by providing a logical and structured pathway through a website.
They guide visitors to related content, helping them explore more pages and engage with the site's offerings.
Improved Page Authority
Internal linking distributes page authority and link equity across a website.
When you link from a high-authority page to another page on the same site, you pass along some of that authority, potentially boosting the linked page's visibility in search results.
Content Relevance
Internal links establish connections between related content. When strategically placed, these links signal to search engines the relationships between different pages, aiding in the interpretation of content relevance.
Reduced Bounce Rate
By providing users with easy access to more content, internal links can help reduce bounce rates. Visitors are more likely to stay on a site longer when they can effortlessly navigate through relevant information.
You can use Website Audit to check the bounce rate for any websites:
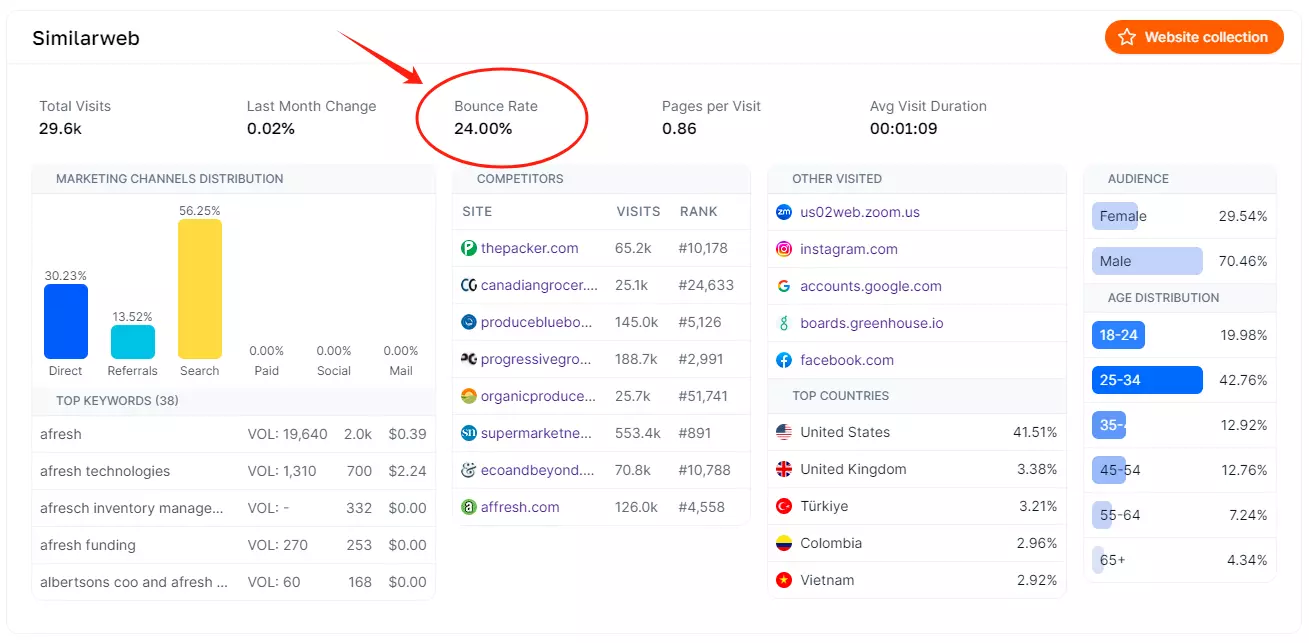
Types of Internal Links
Within the realm of the web, various types of links play essential roles in guiding users through online content.
Navigational Links
The primary means by which visitors navigate a website is through its site navigation. These internal links hold significant importance, serving as the backbone for users to explore different sections of your site.
Contextual Links
Integrated within the main body of content on a webpage, contextual links serve diverse purposes. They can elaborate on concepts, reference additional resources, provide term definitions, or guide readers to other pertinent content.
Here’s an example of a contextual link to another blog in Niche Finder:
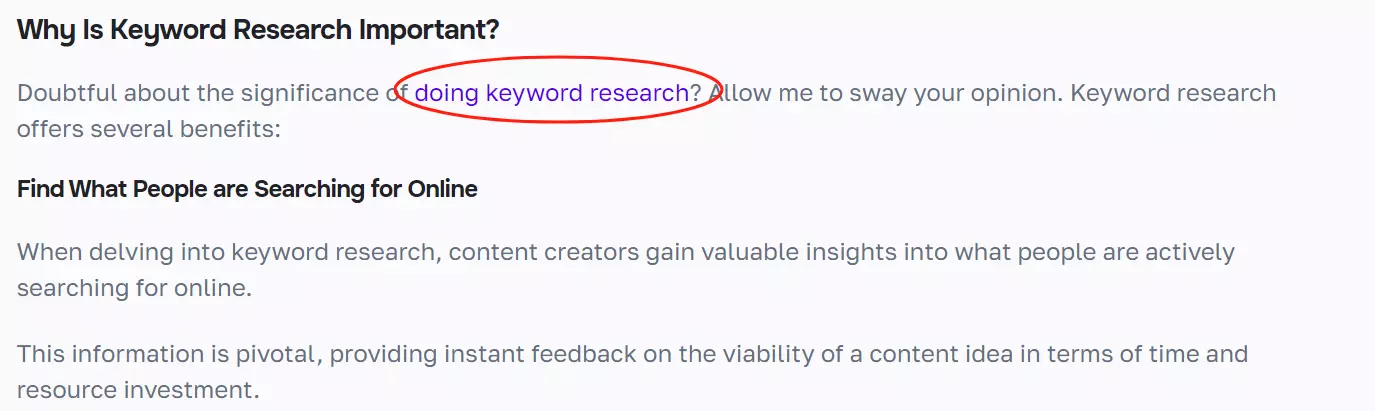
Breadcrumb Links
Establishing connections between pages, and internal links like breadcrumbs enable users to trace their path back to the homepage.
Typically positioned at the top of internal pages such as product pages or blog posts, breadcrumbs are considered regular links by search engines like Google.
Sidebar Links
Often functioning both as contextual links and navigation aids, sidebar links are prevalent on websites with extensive content.
They guide users to popular or relevant content, making them particularly useful for platforms featuring a wide range of articles, such as news or recipe sites.
Footer Links
Positioned at the bottom of a webpage, footer links provide additional pathways for users.
While including links to essential pages like the contact page and privacy policy, they are not the primary navigation method. Instead, footer links offer supplementary details for users seeking further information.
Niche Finder's footer links feature contact information, privacy policy, and other crucial pages.

Internal Linking Best Practices & Tips
How to do internal links? Here are some best SEO practices:
Use Descriptive Anchor Text
Anchor text, the clickable text of a hyperlink, should be descriptive and relevant to the linked page's content. This provides both users and search engines with a clear understanding of the linked page's topic.
Create a Hierarchical Structure
Organize internal links hierarchically, emphasizing the most important pages. This helps search engines understand the structure of your site and prioritize content accordingly.
Link to Relevant Content
Ensure that internal links point to contextually relevant content. Linking to unrelated pages can confuse both users and search engines, affecting the overall coherence of your site.
Read More: How Many Internal Links Per Page SEO?
Optimize Link Placement
Consider the placement of internal links within the content. Links within the body of an article are often more effective than links in navigation menus, as they are contextually integrated.
Strategic Use of Dofollow/Nofollow
For the effective transmission of PageRank, it is essential to employ dofollow links within your internal linking structure. The dofollow attribute serves as a directive for search engine robots, particularly those of Google, indicating that they should follow the links on the page rather than disregard them.
However, there are instances where the judicious use of the nofollow tag becomes relevant. This is particularly applicable to pages that do not require ranking prominence, such as "Thank you" or confirmation pages.
Regularly Update and Audit Links
As your website evolves, regularly audit and update internal links. Broken or outdated links can negatively impact user experience and SEO.
Final Thoughts: What Are Internal Links
In conclusion, internal links are a fundamental element of effective website design and SEO strategy.
They not only enhance navigation and user experience but also play a crucial role in shaping a website's visibility in search engine results.
By understanding the benefits and best practices associated with internal linking, website owners and content creators can harness this powerful tool to create a more cohesive online presence and improve their site's performance in the digital landscape.

